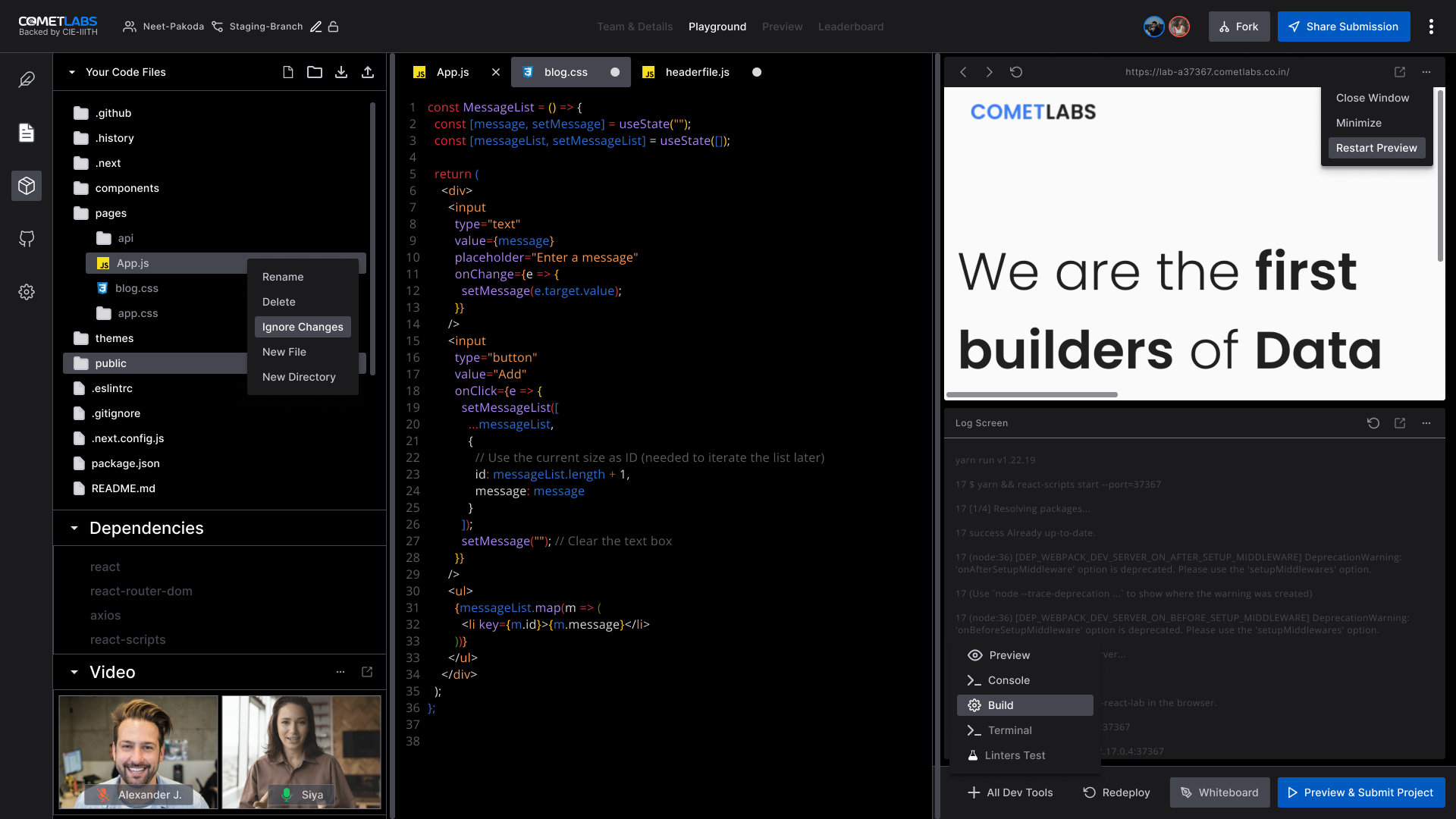
1. Introduction
Objective: Develop a comprehensive cloud-based platform for thorough code analysis that fetches, deploys, and critically analyzes code repositories. This platform aims to leverage both static code analysis tools and dynamic machine learning models to provide detailed insights into code quality and best practices.
Background: In an era of growing software complexity, ensuring code quality becomes challenging. CometLabs seeks to simplify and amplify this process through automation and intelligence.
Target Audience: Software developers, tech leads, hiring managers, tech companies, recruiters, QA engineers, and code reviewers, who are looking for a streamlined process to assess coding skills, project quality, and deploy code in a sandboxed environment.
2. Features and Functionalities
2.1 Cloud IDE and Environment Setup
- Feature: Integrated Development Environment (IDE) in the cloud.
- Functionality: Enable users to write, edit, and debug code directly within the platform, providing a holistic coding experience.
- Sub-features:
- Syntax highlighting for 50+ languages.
- Integrated terminal for command-line operations.
- Debugging tools and console output.
- User Story: As a user, I want to edit my code in a familiar environment with syntax highlighting to quickly spot and fix errors.
2.2 Code Fetching and Deployment
- Feature: Integration with version control platforms.
- Functionality: Fetch repositories from platforms like GitHub, GitLab, and Bitbucket, ensuring seamless access to codebases.
- Sub-features:
- OAuth integration for secure VCS access.
- UI for repository selection and branch specification.
- Code fetching progress bar.
- User Story: As a developer, I want to connect my GitHub account, select repositories for analysis, and deploy them in a sandboxed environment without multiple logins.
2.3 Automated Environment Detection and Setup
- Feature: Environment detection based on the codebase.
- Functionality: Detect the programming language and framework used, automatically setting up the required environment using Docker containers.
- Sub-features:
- Automatic detection of programming language and version.
- Auto-detection of frameworks and libraries.
- One-click environment setup based on detected requirements.
- User Story: As a developer, I want the platform to recognize my project’s tech stack and set up the necessary environment without my intervention.
2.4 Static Code Analysis
- Feature: Code quality assessment.
- Functionality: Utilize tools like ESLint (for JavaScript) to analyze the code for common issues, best practices, and adherence to coding standards.
- Sub-features:
- Customizable linting rules.
- Code smell detection.
- Potential bug identification.
- Code complexity metrics (e.g., cyclomatic complexity).
- User Story: As a team lead, I want to ensure that the code meets our coding standards and best practices.
2.5 Dynamic Code Analysis with Machine Learning
- Feature: Semantic code analysis.
- Functionality: Employ NLP models to understand code semantics, identify intricate coding patterns, and provide a deeper analysis than traditional static tools.
- Sub-features:
- Code pattern recognition.
- Predictive bug detection.
- Recommendations for code optimization.
- Code commentary analysis for sentiment and clarity.
- User Story: As a senior developer, I desire insights beyond traditional static analysis to enhance the overall quality and maintainability of our code.
2.6 Feedback and Continuous Learning
- Feature: User feedback mechanism.
- Functionality: Allow users to provide feedback on the analysis results, enhancing the platform’s accuracy over time.
- Sub-features:
- Feedback forms on analysis accuracy.
- Option to correct false positives/negatives.
- User contribution section for custom linting rules.
- User Story: I want to contribute to the platform’s accuracy as a user, ensuring the community benefits from improved analysis over time.
2.7 Security and Privacy
- Feature: Secure code fetching and analysis.
- Functionality: Ensure all code repositories are processed securely with data encryption and strict access controls.
- Sub-features:
- End-to-end encryption.
- GDPR compliance for data storage and handling.
- Two-factor authentication.
- User Story: As a company CTO, I want to ensure our proprietary code remains secure and private during the analysis process.
3. User Flow
- Login/Register: Users sign up or log in using email or third-party integrations.
- Dashboard: Users are presented with a dashboard showcasing past analyses, feedback, and insights.
- Repository Integration: Users connect their version control platform and select a repository for analysis.
- Analysis: The platform fetches the repository, sets up the environment, runs the code, and commences the analysis.
- Results: Users are provided with a detailed report on code quality, including both static and dynamic analysis results.
- Feedback: Users have the option to provide feedback on the analysis, which aids in refining the platform’s accuracy.
4. Non-Functional Requirements
- Scalability: Designed to accommodate a vast number of simultaneous users and code analyses.
- Performance: Analysis should be swift, offering real-time feedback to users.
- Availability: Strive for an uptime of 99.9%.
- Security: All data, especially code repositories, must be treated with utmost security, ensuring encryption both at rest and in transit.
5. Constraints and Limitations
- Initial support might be restricted to popular languages/frameworks.
- Analysis accuracy can fluctuate based on the codebase’s complexity and the current state of machine learning models.
- Integrating with every version control platform might pose challenges.
6. Future Scope
- Integration with CI/CD: Permit users to weave the platform into their continuous integration and deployment pipelines.
- Custom Rules: Allow users to dictate custom rules for static code analysis.
- Team Collaboration: Enable multiple users to collaborate on a single analysis, making it apt for team-based projects.
7. Performance Metrics & KPIs
- User Acquisition: Monitor the number of new sign-ups.
- Active Users: Keep tabs on daily and monthly active users.
- Analysis Accuracy: Measure the accuracy of both static and dynamic code analyses via user feedback.
- Server Uptime: Ensure 99.9% uptime.
- Response Time: Aim for sub-second response times for code fetching and initiating analysis.
8. Milestones and Timeline
- Q1: Infrastructure setup, initial cloud IDE development, and version control integrations.
- Q2: Static code analysis tools deployment and preliminary machine learning model training.
- Q3: Beta version launch, user feedback aggregation, and iterative enhancements.
- Q4: Complete launch with all features, alongside marketing campaigns and user acquisition initiatives.
9. Rollout Strategy
Alpha Testing: Internal testing within the CometLabs team.
- Beta Testing: Closed beta with chosen users for gathering feedback.
- Public Launch: Full release accompanied by marketing campaigns.
- Iterative Improvements: Regular updates are influenced by user feedback and emerging technological trends.
10. Budget and Resource Allocation
A meticulous budget breakdown, including:
- Development Costs: Staff salaries, subscriptions to third-party tools.
- Infrastructure Costs: Hosting, databases, storage.
- Marketing Costs: Campaigns, advertisements, events.
- Miscellaneous Costs: Licenses, audits, third-party integrations.
11. Technical Architecture
A comprehensive breakdown of the technical stack:
- Frontend: Technologies such as React or Vue.js for the web interface.
- Backend: Node.js or Django for server operations.
- Database: PostgreSQL or MongoDB for storing user data, feedback, and analysis results.
- ML Models: TensorFlow or PyTorch for the training and deployment of machine learning models.
- Infrastructure: AWS or Google Cloud for hosting, Docker for containerization.
12. Conclusion
The CometLabs Code Analysis and Deployment Platform is envisioned to transform code assessments by amalgamating traditional static analysis with advanced machine learning insights. By offering detailed, actionable feedback to developers and other stakeholders, the platform seeks to become an essential tool for code quality assurance, hiring, and education. With an emphasis on user experience, accuracy, and analytics, it is poised to become an indispensable resource for developers and companies alike.